Introduction
Understanding what was the first animal on Earth is a fascinating journey into the depths of biological history. The quest to identify the earliest creature that could be classified as an animal uncovers a narrative filled with scientific exploration and discovery. This article delves into the origins of life, highlighting pivotal findings and theories about the first animal and its significance in the broader context of evolution.
Key Takeaways:
- The first animal on Earth was likely a simple, sponge-like organism.
- Understanding early animals helps us grasp the complexity of evolution.
- Early life forms had a profound impact on Earth’s biological and ecological systems.
1. The Origins of Life on Earth
The story of life on Earth begins with the formation of our planet around 4.5 billion years ago. The earliest forms of life were simple, single-celled organisms that emerged in the primordial soup of early oceans. These primordial life forms set the stage for the development of more complex organisms.
Key Points:
- Early Life Forms: Simple, single-celled organisms like bacteria and archaea.
- Conditions for Life: The primordial soup theory suggests that life began in a nutrient-rich environment.
2. Defining What Constitutes an Animal
To answer the question of what was the first animal on Earth, it’s essential to define what constitutes an animal. Animals are multicellular organisms that have specialized tissues and organs. Unlike plants and fungi, animals are primarily heterotrophic, meaning they consume other organisms for energy.
Key Points:
- Multicellularity: Animals are composed of multiple cells with specialized functions.
- Heterotrophy: Animals rely on consuming other organisms for energy.
3. The First Evidence of Multicellular Life
The transition from single-celled to multicellular life was a significant evolutionary step. Fossil evidence suggests that the first multicellular organisms appeared around 600 million years ago. These early multicellular life forms paved the way for more complex animal life.

Key Points:
- Early Multicellular Life: Organisms like Dickinsonia and other early Ediacaran fauna.
- Fossil Evidence: Fossils provide clues about early multicellular organisms.
4. The Ediacaran Period: The Dawn of Complex Life
The Ediacaran period, which occurred approximately 635 to 541 million years ago, was a crucial time in the history of life. During this period, the first complex multicellular organisms appeared, many of which are considered to be the earliest animals.
Key Points:
- Ediacaran Fauna: Early complex multicellular organisms with unique body plans.
- Significance: Represents a critical stage in the evolution of animal life.
5. The Cambrian Explosion: A Burst of Diversity
Around 541 million years ago, the Cambrian Explosion marked a rapid diversification of life forms, leading to the appearance of many of the major animal groups we recognize today. This period is crucial for understanding what was the first animal on Earth.
Key Points:
- Cambrian Explosion: A rapid increase in the diversity of animal life.
- Early Animals: Emergence of various phyla including arthropods, mollusks, and chordates.
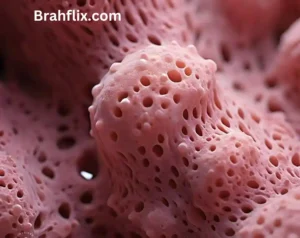
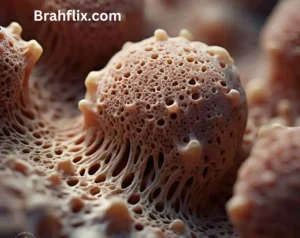
6. The First True Animals: Sponges and Other Early Life Forms
Sponges, belonging to the phylum Porifera, are often considered among the first true animals. They are simple, multicellular organisms with a porous structure that allows them to filter nutrients from the water.
Key Points:
- Sponges: Simple, multicellular organisms with a porous structure.
- Other Early Animals: Includes early cnidarians like jellyfish.
7. The Role of Genetics in Identifying Early Animals
Advances in genetic research have provided insights into the evolutionary relationships between early animals and their modern descendants. By comparing genetic material, scientists can trace the lineage of the first animals.
Key Points:
- Genetic Markers: Used to trace evolutionary relationships.
- Evolutionary Trees: Help map the development of early animals.
8. Impact of Early Animals on Earth’s Ecosystems
The emergence of the first animals had a profound impact on Earth’s ecosystems. Early animals contributed to the development of complex ecological interactions and influenced the formation of early marine environments.
Key Points:
- Ecological Impact: Early animals contributed to the development of marine ecosystems.
- Biological Interactions: Formation of food webs and predator-prey relationships.
9. The Evolutionary Legacy of the First Animals
The legacy of the first animals is evident in the diversity of life forms that followed. Early animals laid the groundwork for the development of more complex organisms and ecosystems, influencing the course of evolutionary history.
Key Points:
- Evolutionary Influence: Early animals set the stage for future evolutionary developments.
- Diverse Descendants: Modern animals share a common ancestry with early life forms.
FAQs
What was the first known animal on Earth?
The first known animals are believed to be simple, sponge-like organisms from the Ediacaran period.
How did early animals impact Earth’s ecosystems?
Early animals contributed to the development of complex ecosystems, influencing marine environments and ecological interactions.
What was the Cambrian Explosion?
The Cambrian Explosion was a period of rapid diversification of life forms, leading to the emergence of many major animal groups.
How do scientists determine the lineage of early animals?
Scientists use genetic markers and evolutionary trees to trace the lineage and relationships of early animals.
Why are sponges considered among the first true animals?
Sponges are considered among the first true animals due to their simple, multicellular structure and filter-feeding mechanism.
Conclusion
In exploring what was the first animal on Earth, we uncover a rich history of early life forms that set the stage for the complex biodiversity we see today. From the primordial soup of early Earth to the explosion of life during the Cambrian period, the journey of the first animals is a testament to the intricate web of evolution. Understanding these early organisms not only highlights their significance but also provides insight into the ongoing story of life on our planet.
Questions for Readers:
- What do you find most intriguing about the origins of early animals?
- How do you think early animals influenced modern ecosystems?
Call to Action: For more fascinating insights into the history of life and evolution, check out our other blog posts and join the conversation about the wonders of our natural world!