Introduction
Understanding demographic concepts like population density and population distribution is essential for analyzing human settlements and planning urban environments. These terms often come up in discussions about geography, urban planning, and social sciences, but they are frequently confused. This article will clarify the What is the Difference Between Population Density and Population Distribution, providing a comprehensive overview of each term, their significance, and real-world applications.
Key Takeaways:
- Population density refers to the number of people living per unit area.
- Population distribution describes how people are spread across a region or area.
- Both concepts influence urban planning, resource allocation, and social policies.
What is Population Density?
Population density is a measure that indicates the number of individuals living in a specific area, usually expressed as people per square kilometer or square mile. It provides insight into how crowded or sparsely populated a region is.
Calculating Population Density
Importance of Population Density
- Urban Planning: Helps in designing infrastructure and public services to meet the needs of densely populated areas.
- Resource Allocation: Guides the distribution of resources like water, electricity, and healthcare.
- Environmental Impact: High population density can lead to increased pollution and strain on natural resources.
Examples and Statistics
According to the World Bank, countries like Monaco and Singapore have some of the highest population densities globally, exceeding 20,000 people per square kilometer. In contrast, countries like Canada and Australia have much lower densities, often below 5 people per square kilometer.
What is Population Distribution?
Population distribution refers to the pattern of where people live within a specific area. Unlike density, which is a quantitative measure, distribution is about the spatial arrangement of people across different regions.
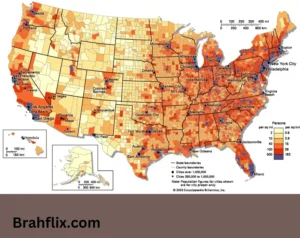
Patterns of Population Distribution
Population distribution can be categorized into several patterns:
- Uniform Distribution: People are evenly spread across an area. This is rare and often seen in agricultural communities.
- Clustered Distribution: People are concentrated in specific areas, such as cities or towns.
- Random Distribution: People are spread without any discernible pattern. This is common in less developed or rural areas.
Importance of Population Distribution
- Urban Planning: Helps in understanding where to build new infrastructure and services.
- Economic Development: Influences market size and economic activities in different regions.
- Emergency Planning: Assists in planning for evacuations and disaster response based on population clusters.
Examples and Statistics
In the United States, population distribution is highly uneven, with the majority of people living in metropolitan areas such as New York City and Los Angeles, while vast rural areas like the Great Plains have lower populations.
What is the Difference Between Population Density and Population Distribution
While population density and population distribution are related, they describe different aspects of how people live within a region.
1. Definition and Focus
- Population Density: Focuses on the number of people per unit area. It is a quantitative measure.
- Population Distribution: Focuses on how people are spread out across an area. It describes patterns rather than numbers.
2. Measurement and Analysis
- Population Density: Measured using specific numerical data and calculations.
- Population Distribution: Analyzed through patterns and geographic layouts, often visualized through maps.
3. Impact and Applications
- Population Density: Influences infrastructure needs, environmental impact, and resource management.
- Population Distribution: Affects urban planning, economic activities, and emergency management.
Table: Comparison of Population Density and Distribution
| Aspect | Population Density | Population Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of people per unit area | Spatial arrangement of people |
| Measurement | Quantitative (e.g., people/sq km) | Descriptive (e.g., clustered, random) |
| Impact | Infrastructure, resources, environmental issues | Urban planning, economic activities, emergency planning |
Factors Influencing Population Density
Several factors contribute to variations in population density across different regions:
1. Geographic Features
- Topography: Mountains, rivers, and other natural barriers can limit settlement and affect density.
- Climate: Extreme weather conditions can make areas less hospitable, affecting population concentration.
2. Economic Opportunities
- Employment: Areas with more job opportunities tend to have higher population densities.
- Services: Regions with better healthcare, education, and recreational facilities attract more residents.
3. Government Policies
- Urbanization Policies: Policies promoting city development can lead to higher densities in urban areas.
- Housing Policies: Availability and affordability of housing impact population density in various regions.
Factors Influencing Population Distribution

Population distribution is shaped by several factors, including:
1. Economic Factors
- Employment Opportunities: People tend to cluster in areas with better job prospects.
- Cost of Living: High costs in certain regions can lead to lower population density.
2. Social and Cultural Factors
- Family Ties: People often live near family and friends, influencing distribution patterns.
- Cultural and Historical Significance: Certain areas may attract people due to cultural or historical reasons.
3. Government and Infrastructure
- Transportation: Good transportation links can lead to more even distribution across a region.
- Urban Development: Planned developments and new towns can alter existing distribution patterns.
Table: Factors Influencing Population Distribution
| Factor | Impact on Population Distribution |
|---|---|
| Economic Opportunities | Higher density in economically thriving areas |
| Social Factors | Clusters around family and cultural centers |
| Infrastructure | More even distribution with better transportation and urban planning |
Real-World Applications and Examples
Urban Planning
Understanding both population density and population distribution is crucial for urban planners. High density in urban areas may necessitate the development of vertical housing and efficient public transport, while distributed populations in rural areas may require different infrastructure investments.
Resource Management
Efficient resource management relies on both concepts. For example, high-density areas may need advanced waste management systems, while sparsely populated regions might focus on improving connectivity and access to resources.
Environmental Impact
Population density can affect environmental sustainability, with densely populated areas experiencing higher pollution levels and resource depletion. Population distribution influences land use and conservation efforts, with distributed populations potentially impacting larger areas.
FAQs
What is the primary difference between population density and population distribution?
Population density measures how many people live in a specific area, while population distribution describes how people are spread across a region.
How does population density affect urban planning?
High population density can lead to increased demand for infrastructure, housing, and public services, requiring careful urban planning to manage resources effectively.
What are some common patterns of population distribution?
Common patterns include uniform, clustered, and random distributions, each affecting how people interact with their environment and access resources.
Why is understanding population distribution important for emergency planning?
Knowing population distribution helps in planning for evacuations, resource allocation, and disaster response, ensuring that help reaches those who need it most efficiently.
How do geographic and economic factors influence population density?
Geographic features like mountains and climate can limit settlement areas, while economic opportunities and living costs influence where people choose to live.
Conclusion
In summary, population density and population distribution are distinct yet interconnected concepts that provide valuable insights into human settlements. Understanding these differences helps in effective urban planning, resource management, and addressing environmental challenges.
Population density provides a quantitative measure of how crowded an area is, while population distribution describes the spatial arrangement of people across a region. Both factors play a crucial role in shaping our cities and communities.
We’d love to hear your thoughts! How do you think population density and distribution impact your community? Feel free to share your experiences and insights.
For more articles on related topics, check out our blog and stay informed about the latest trends in geography and urban planning.
